
- #Light sequencing ladder logic program examples code#
- #Light sequencing ladder logic program examples series#
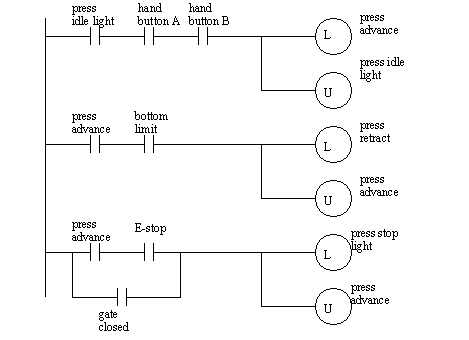
Without a path of true instructions from left to right, the output on rung three, O:2/2, is off. The XIO representing I:1/3 is true because the input device it represents is open. Therefore, because I:1/1 and I:1/2 are both closed, the XIO instructions representing those inputs are false. In the case of internal bits, this instruction is true if the internal bit is off. The XIO will be true only if the input connected to it is open. The third rung introduces the XIO instruction. An XIO instruction is best described as true if open.įigure 4. The third rung introduces the XIO instruction. This is the basic structure of all ladder logic programs. Thus, output O:2/1 will be true if I:1/3 is true OR if both I:1/1 AND I:1/2 are true. This second rung could be rewritten without the internal bit by replacing B:0/1 with the two inputs from rung one. O:2/1 is an output instruction that represents channel 1 on a physical discrete output card placed in slot 2. These two inputs are placed in parallel and represent an OR condition. The second rung represents a third input used with an input instruction. On the second rung, we have a third input labeled I:1/3 and our internal bit is now used with an input instruction instead of an output.įigure 3.

That’s why it’s labeled B instead of O for “output.” These internal bits work great when a certain state or set of inputs needs to be recorded without actually turning on a physical output. The output in this case, B:0/1, is actually an internal bit stored in the PLC's memory. Therefore, the output on rung one will be true because a path of true instructions, I:1/1 and I:1/2, exists. The only way for an output to be energized is if a path of true instructions can be traced from the left rail to the right rail. If an instruction is true it is highlighted in green. That is, this instruction will be true if the input device it represents is closed. An XIC instruction really means true if closed. The second input represents channel 2 on the same card. Input cards have more than one channel, and if the instruction specifies /1, the instruction accesses channel 1. I:1 means that this input card has been placed in slot 1, directly adjacent to the processor. The first rung represents a physical input found on one of the discrete input cards. This instruction represents a physical input found on one of the discrete input cards.įigure 2. The symbol is an XIC, and the I denotes that this is an input. Looking at the first rung, notice the first two inputs I:1/1 and I:1/2. The symbols placed throughout the rungs are actually graphical instructions. The program is “scanned” or run by the CPU from left to right and top to bottom. This ladder logic program is three rungs long. Let’s take a look at an example of ladder logic programming: As with real relays, there are normally open contacts and normally closed contacts.
#Light sequencing ladder logic program examples series#
Contacts are placed in series to represent AND logic and in parallel when using OR logic.
#Light sequencing ladder logic program examples code#
This bit can then be used later on in the code as another input. Outputs don't have to be physical, though, and can represent a single bit in the PLC's memory. The contacts act as inputs and often represent switches or push-buttons the coils behave as outputs such as a light or a motor. Along the rungs are contacts and coils, modeled after the contacts and coils found on mechanical relays. It uses long rungs laid out between two vertical bars representing system power. Of the various languages one can use to program a PLC, ladder logic is the only one directly modeled after electromechanical relay systems. Programmable logic controllers or PLCs are digital computers used to perform control functions, usually for industrial applications. This article will briefly describe what ladder logic is and go over some examples of how it functions. Ladder diagram, better known as ladder logic, is a programming language used to program PLCs (programmable logic controllers).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
